FOOT : FragmentatiOn Of Target experiment
par
Amphi Kastler
Subatech IMT Atlantique
The interest in the study of the mechanisms underlying the ion fragmentation in collisions at energies in the particle therapy applications range (60–400 MeV/u) and in the radioprotection system range (400-1000 MeV/u) has been constantly rising in the recent past, where an improved description of the heavy ions interactions with matter is eagerly needed.
Monte Carlo is commonly considered as the gold standard for treatment planning system, as it accounts for the physics of the different particles interactions. However, the constraints on nuclear models and fragmentation cross sections in the energy range used in hadrontherapy are not yet sufficient to reproduce the fragmentation processes with the required accuracy for clinical treatments. Therefore, measurements are necessary to benchmark the simulation in this energy range.
The aim of the FOOT experiment is to measure differential cross sections in inverse and direct kinematic, e.g., different beams (carbon, oxygen ions) on hydrogenous targets (polyethylene).
The electronic setup of the FOOT experiment, complemented by an emulsion setup, is composed, downstream, by a start counter, a beam monitor, a tracking system (pixel/strip silicon detectors) embedded in a magnetic field, a time of flight and calorimeter (see fig. 1).
Performances of the different sub-detectors will be presented as well as results in term of differential cross section measurements obtained during the last campaigns.
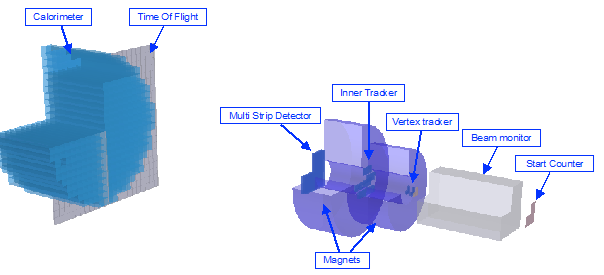
Figure 1: Setup of FOOT experiment including the start counter, the beam monitor, the vertex tracker, the inner tracker, the multi strip detector, the time of flight and the calorimeter. The magnetic field is induced by two permanent magnets.